Turning Ideas Into Digital Experiences
We craft modern web and mobile applications that drive your business forward with cutting-edge technology and innovative design
100+
Projects Delivered
50+
Happy Clients
24/7
Support Available
What We Do
We specialize in creating digital solutions that make a difference
Web Development
Custom web applications built with modern technologies, scalable architecture, and exceptional user experience.
Learn More →Mobile Apps
Native and cross-platform mobile applications that engage users and deliver seamless performance.
Learn More →UI/UX Design
Intuitive and beautiful designs that put users first, creating experiences that delight and convert.
Learn More →AI-Powered Development
We leverage cutting-edge AI tools and technologies to accelerate our development process, delivering high-quality solutions faster and more efficiently than traditional methods.
Productivity Boost
Faster Delivery
Code Quality

Rapid Development
AI-assisted coding accelerates development without compromising quality
Smart Solutions
Intelligent code suggestions and optimizations for better performance
Enhanced Security
AI-powered security analysis to identify and fix vulnerabilities
Why Choose FreshyPortal?
We bring expertise, innovation, and dedication to every project
Fast Delivery
Agile development process ensures quick turnaround times
Secure & Reliable
Enterprise-grade security and robust architecture
Expert Team
Skilled developers with years of industry experience
24/7 Support
Dedicated support team always ready to help
Recent Works
Projects that showcase our expertise
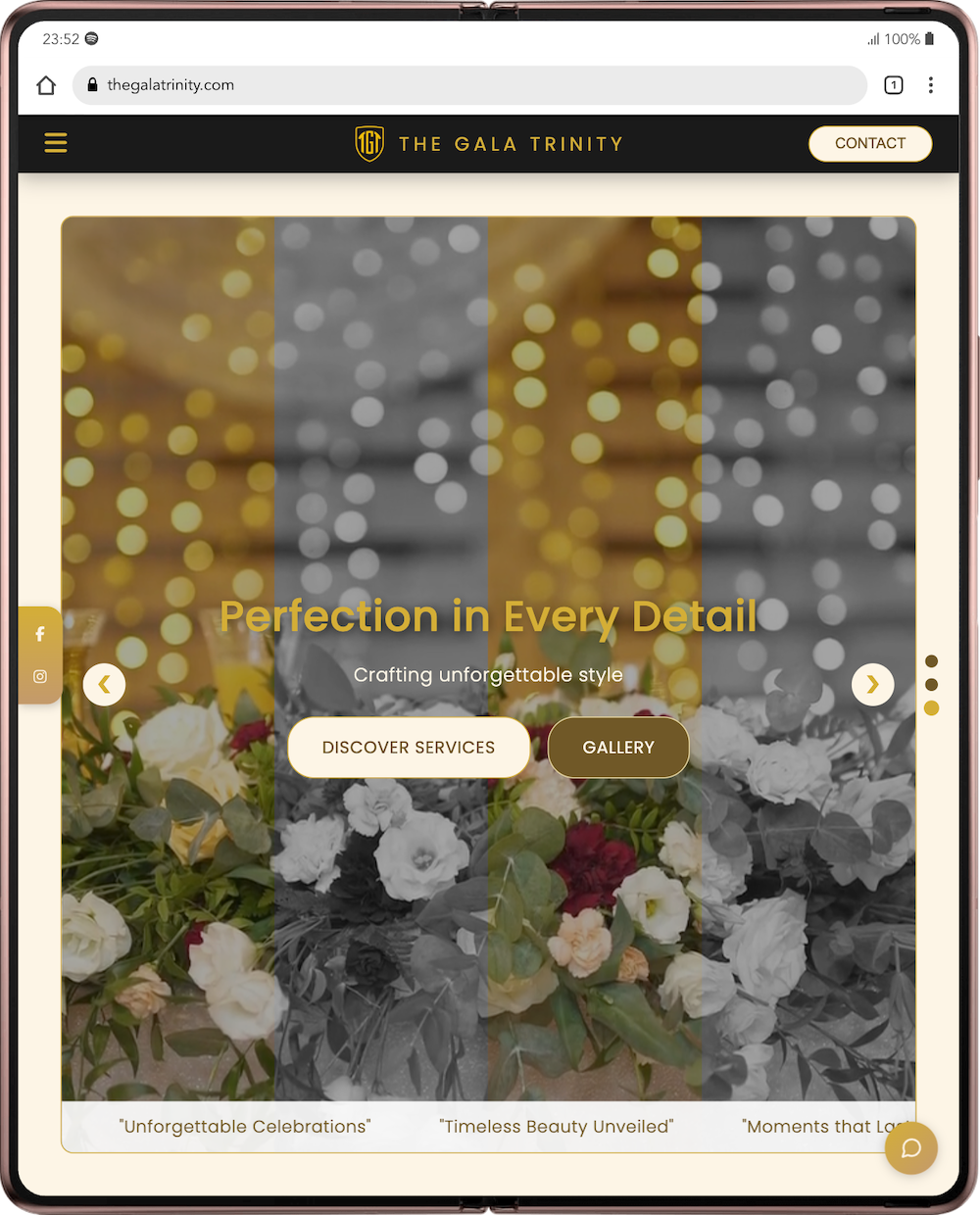

The Gala Trinity
Event ManagementPremium event management services with creativity and precision. We specialize in corporate events, weddings, and luxury celebrations with a focus on delivering unforgettable experiences.
Our Products
Empowering the internet with free tools made by FreshyPortal
Triniva.com
LiveProfessional PDF tools suite offering comprehensive document management solutions. Merge, split, compress, and convert PDFs with advanced features for seamless workflow optimization.
HRera.com
Coming SoonModern recruitment platform designed for HR agencies to streamline their hiring process. Features intelligent candidate matching, automated workflows, and comprehensive analytics for efficient talent acquisition.
RashiPatrika.com
LiveComprehensive astrology platform providing personalized horoscopes, free Kundli charts, and compatibility matching. Features multi-language support, AI-powered predictions, and educational content for seamless spiritual guidance.
What Our Clients Say
Success stories from businesses we've helped transform
"FreshyPortal transformed our online presence. Their team delivered a stunning website that exceeded our expectations."
"The mobile app they developed has been a game-changer for our business. Professional, fast, and reliable!"
"Outstanding UI/UX design and seamless development process. Highly recommend FreshyPortal!"
Ready to Start Your Project?
Let's turn your ideas into reality. Get in touch with us today!
Contact Us Now